resilience4j 源码还是比较清晰简单的,比较适合阅读。
放一张主要类的结构图:
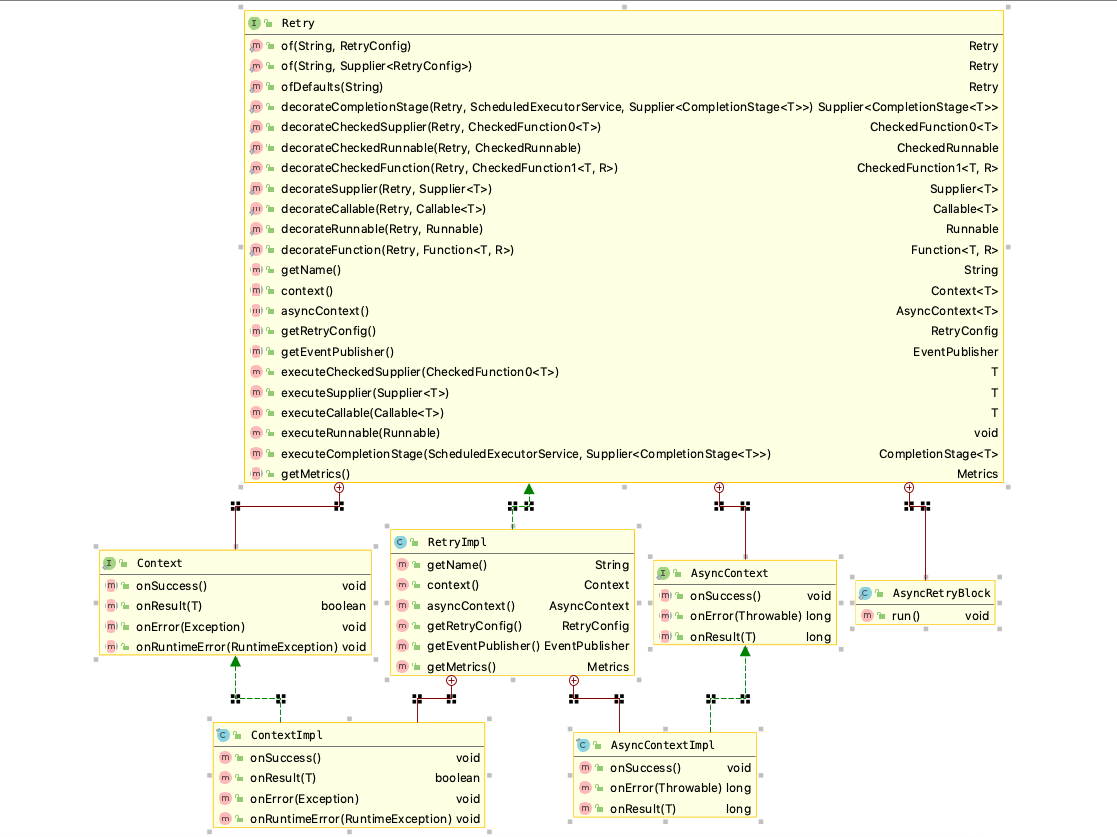
Retry入口
Retry接口是提供重试功能的入口,主要提供了方法模版,具体校验结构,失败后处理由Context子类实现。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
static <T> Supplier<T> decorateSupplier(Retry retry, Supplier<T> supplier) {
return () -> {
Retry.Context<T> context = retry.context();
do try {
T result = supplier.get();
final boolean validationOfResult = context.onResult(result);
if (!validationOfResult) {
context.onSuccess();
return result;
}
} catch (RuntimeException runtimeException) {
context.onRuntimeError(runtimeException);
} while (true);
};
}
|
这里摘抄了一段核心代码,作用是循环直到context.onResult(result)返回true为止,需要留意context.onResult/onRuntimeError/onError可能执行多次, onSuccess只会执行一次,这里每次进入重试都是一个新的context对象。
Retry.ContextImpl
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| public boolean onResult(T result) {
if (null != resultPredicate && resultPredicate.test(result)) {
int currentNumOfAttempts = numOfAttempts.incrementAndGet();
if (currentNumOfAttempts >= maxAttempts) {
return false;
} else {
waitIntervalAfterFailure(currentNumOfAttempts, null);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public void onRuntimeError(RuntimeException runtimeException) {
if (exceptionPredicate.test(runtimeException)) {
lastRuntimeException.set(runtimeException);
throwOrSleepAfterRuntimeException();
} else {
failedWithoutRetryCounter.increment();
publishRetryEvent(() -> new RetryOnIgnoredErrorEvent(getName(), runtimeException));
throw runtimeException;
}
}
|
先关注onResult,它负责判断是否需要继续重试,如果通过校验或者重试超过此数,会停止重试。
onRuntimeError/onError, 负责把catch的异常存储在lastRuntimeException中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public void onSuccess() {
int currentNumOfAttempts = numOfAttempts.get();
if (currentNumOfAttempts > 0) {
succeededAfterRetryCounter.increment();
Throwable throwable = Option.of(lastException.get()).getOrElse(lastRuntimeException.get());
publishRetryEvent(() -> new RetryOnSuccessEvent(getName(), currentNumOfAttempts, throwable));
} else {
succeededWithoutRetryCounter.increment();
}
}
|
onSuccess负责统计和发送事件。
总结
总体来说retry比较简单,需要注意的点有一个如果设置了结果校验,如果一直校验不通过,将返回未通过的结果,而不是返回失败。
